The project's main objective is to develop an inventory management system for small businesses to track their warehouse inventory efficiently and avoid out-of-stock issues. The solution also leverages IoT, Model-driven Software Development, and Software System Verification and Analysis concepts.
Smart Rack Project
Section 1: Introduction
The Smart Rack project aims to create an inventory management system with elements from the Internet of Things (IoT), Model-driven Software Development (MDSD), and Software System Analysis and Verification (SSAV) courses. The project is designed to provide an overview of inventory stock for small businesses and assist in avoiding out-of-stock issues.
Section 1.1: Project Purpose
The project’s primary purpose is to develop an inventory management system that leverages IoT, MDSD, and SSAV concepts. This system will help small businesses manage their inventory effectively and address restocking issues.
Section 1.2: Problem Statement
The problem to be addressed is the need for small businesses to have a system that offers insights into their inventory and helps them avoid running out of stock. The solution should incorporate IoT, MDSD, and SSAV elements.
Section 1.3: Overview of the Solution
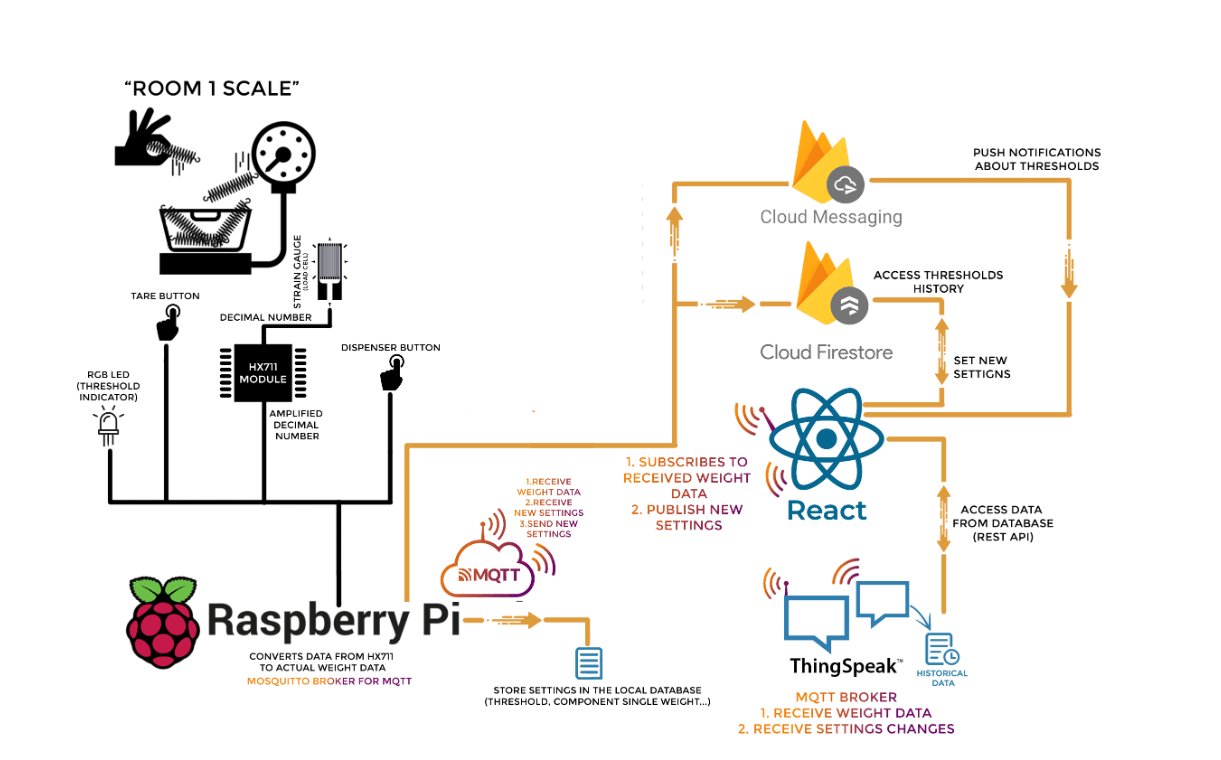
The Smart Rack project comprises both hardware and software components. It combines sensors, Raspberry Pi (RPi), MQTT, and a web application to create a comprehensive solution for inventory management.
Section 1.4: Detailed Project Description
1.4.1: Hardware Components
- Hardware components include weight sensors and a Raspberry Pi (RPi).
- RPi connects to the HX711 sensor for weight data and has an RGB LED for threshold visualization.
1.4.2: Data Flow
- The hardware collects data from sensors and sends it to the web application via MQTT messaging.
- The web application interfaces with Firebase for user authentication and Firestore for data storage.
Section 2: Software Solution
This section delves into the software part of the Smart Rack project, explaining the front-end and back-end implementations, including Firebase integration, React application setup, MQTT configuration, and more.
2.1: Front-end Implementation
- Firebase Integration: A Firebase project is created for authentication and Firestore database.
- React Application: React Router, React Redux, and Redux Thunk are used to manage states and enable asynchronous logic.
- MQTT.js library is added for MQTT communication.
2.2: MQTT Configuration
- MQTT Broker: Configured using ThingSpeak IoT platform for publish/subscribe communication.
- Updates Container Settings: User changes are written to Firestore, and the web-app notifies the back-end via MQTT.
2.3: Sending Scale Updates
- Raspberry Pi publishes changes in weight to ThingSpeak Publish Channel Field Feed.
2.4: Back-end Implementation
- Raspberry Pi and HX711 setup is explained, including Ethernet interface and security measures.
- MQTT and RPi: Paho MQTT Python library is used for MQTT communication.
- Configuration of the HX711 sensor on the Raspberry Pi.
2.5: Domain Specific Language (DSL)
- An external DSL is created using Xtext for generating code to add containers and graph their weight.
2.6: Testing and Evaluation
- Simulation using UPPAAL for comprehensive testing.
- Verification tests include checking for deadlocks, reading speed, error handling, authentication, and notifications.
Section 3: Conclusion
The project successfully addresses the inventory management problem, offering an overview of containers and aiding in restocking. It incorporates IoT, MDSD, and SSAV elements in the hardware, DSL, and testing. The project demonstrates a comprehensive solution for inventory management, combining various elements from IoT, MDSD, and SSAV courses.
Section 3.1: Internet of Things (IoT)
- Elements from the IoT course are incorporated, primarily in the hardware and data transport.
Section 3.2: Model-driven Software Development (MDSD)
- MDSD is applied through the creation of an external DSL used for generating code related to containers and weight graphing.
Section 3.3: Software System Analysis and Verification (SSAV)
- SSAV is used for testing, simulation, and verification, ensuring the system functions correctly.
Section 4: References
The document includes references to sources and materials used in the project.





